03 - Taikun Ingress - basics
Taikun CloudWorks recommends using Ingress as the preferred method for exposing applications to the internet.
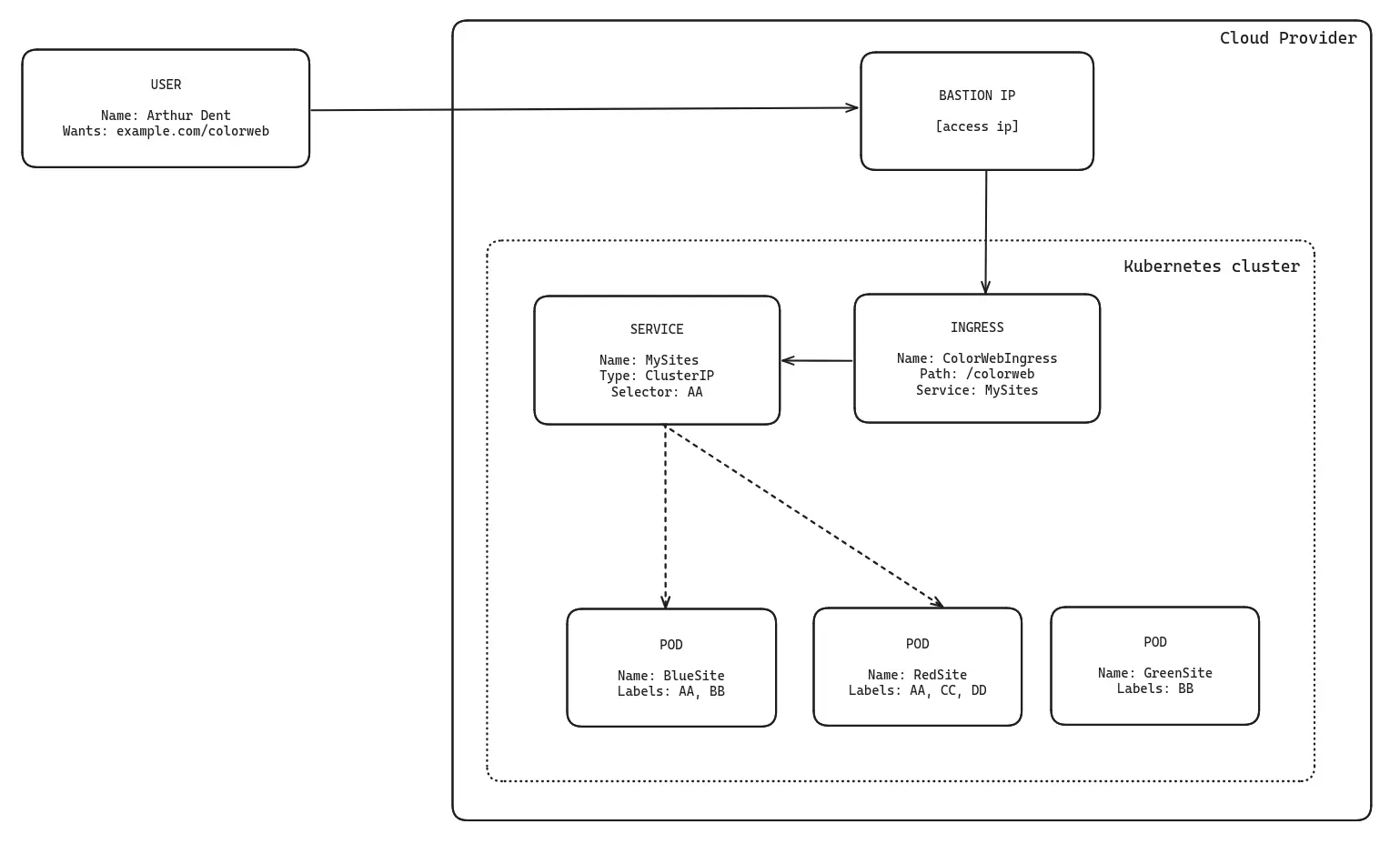
Ingress is a Kubernetes resource that provides routing to services within a cluster. It maps human-readable URLs to Kubernetes ClusterIP services, which in turn route traffic to the appropriate pods.
Example flow:
Human-readable URL → Ingress → ClusterIP Service → Pods
Bastion Architecture
A domain name must ultimately resolve to an IP address. In CloudWorks, this is addressed efficiently without allocating a dedicated public IP for each service.
Each CloudWorks cluster includes a bastion server, which acts as a secure gateway and the sole public entry point to the cluster. This bastion server is the only component with an external IP address (referred to as the Access IP). The cluster nodes themselves do not have public IPs.
Preconfigured Ingress Controller
Every CloudWorks cluster comes with a preconfigured Ingress controller that routes traffic through the bastion’s external IP. This controller uses the Ingress class taikun, commonly referred to as Taikun Ingress.
Benefits
- Stable Access IP: The bastion’s IP remains constant regardless of how many Ingress resources or services you create or remove.
- Simplified DNS Configuration: You only need to point your DNS records to the bastion’s Access IP. All routing is then handled within Kubernetes using Ingress rules.
How it works
Lab excercise:
1. Create a deployment and service in LiveOps
- Expose deployment and service of type LoadBalancer
- the labels on pods MUST match the selector in the service
Example of nginx deployment
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: ingress-test
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: ingress-test
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: ingress-test #All Pods created by this deployment will have label app:ingress-test
spec:
containers:
- name: my-container
image: nginx:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 80
Example of LoadBalancer service
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: ingress-test-svc
spec:
selector:
app: ingress-test #Send packets to Pods that have the app:ingress-test label
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 80
2. Create an Ingress Resource
Example of Ingress
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: ingress-test
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /
spec:
ingressClassName: taikun
rules:
- http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: ingress-test-svc
port:
number: 80
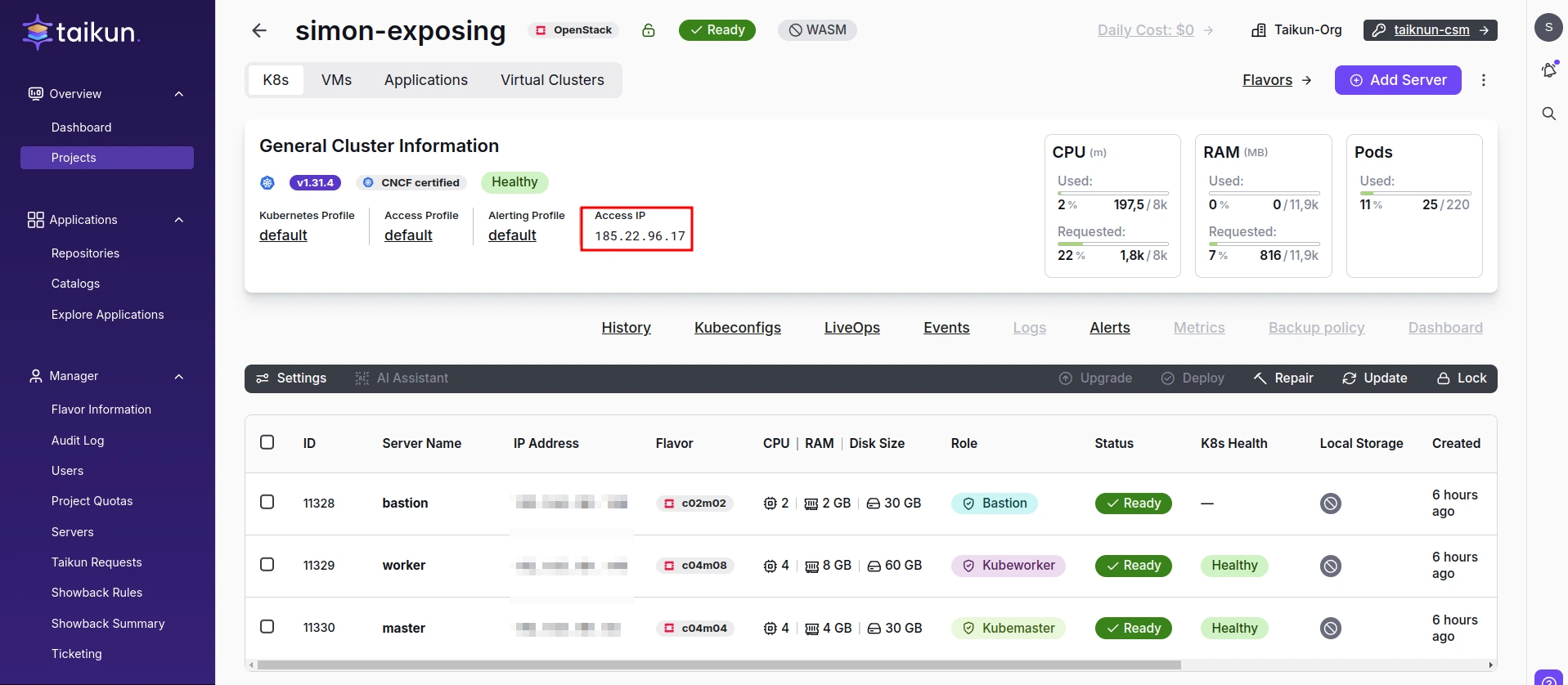
3. (optional) Set up DNS
- Point your DNS to the Bastion IP address of your cluster.
Bastion IP as Access IP
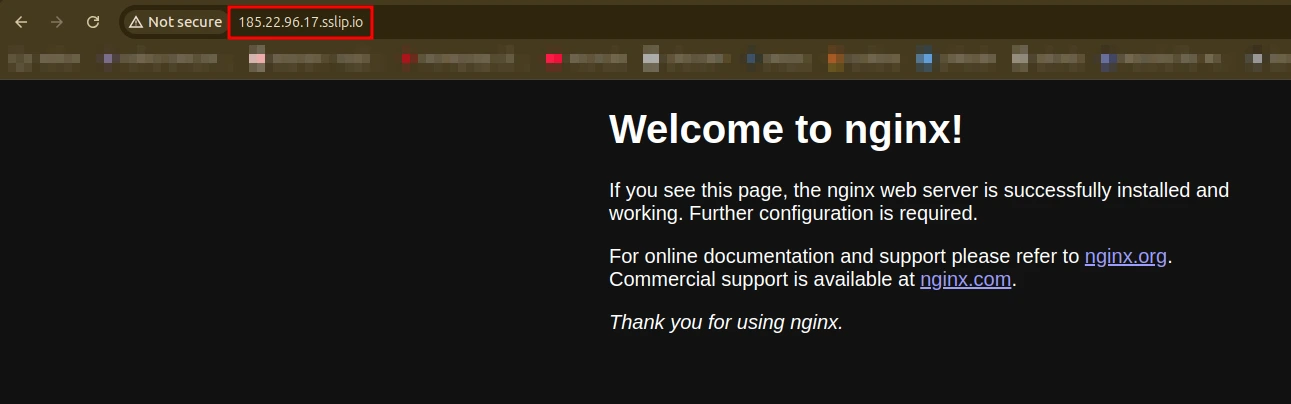
4. Access the Service on your Browser
- If you do not have a custom DNS, use a
sslip.iowildcard domain that resolves automatically (e.g.,x.x.x.x.sslip.io, replacingx.x.x.xwith the Bastion IP) - Open a web browser and navigate to:
- You will see the application served by your deployment.
Access in browser using sslip.io